What is Cloud Computing
The term cloud refers to a network or the internet. It is a technology that uses remote servers on the internet to store, manage, and access data online rather than local drives. The data can be anything such as files, images, documents, audio, video, and more.
There are the following operations that we can do using cloud computing:
- Developing new applications and services
- Storage, back up, and recovery of data
- Hosting blogs and websites
- Delivery of software on demand
- Analysis of data
- Streaming videos and audios
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The characteristics of cloud computing are given below:
1) Agility
The cloud works in a distributed computing environment. It shares resources among users and works very fast.
2) High availability and reliability
The availability of servers is high and more reliable because the chances of infrastructure failure are minimum.
3) High Scalability
Cloud offers "on-demand" provisioning of resources on a large scale, without having engineers for peak loads.
4) Multi-Sharing
With the help of cloud computing, multiple users and applications can work more efficiently with cost reductions by sharing common infrastructure.
5) Device and Location Independence
Cloud computing enables the users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they use e.g. PC, mobile phone, etc. As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.
6) Maintenance
Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, since they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places. So, it reduces the cost also.
7) Low Cost
By using cloud computing, the cost will be reduced because to take the services of cloud computing, IT company need not to set its own infrastructure and pay-as-per usage of resources.
8) Services in the pay-per-use mode
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are provided to the users so that they can access services on the cloud by using these APIs and pay the charges as per the usage of services.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
As we all know that Cloud computing is trending technology. Almost every company switched their services on the cloud to rise the company growth.
Here, we are going to discuss some important advantages of Cloud Computing-
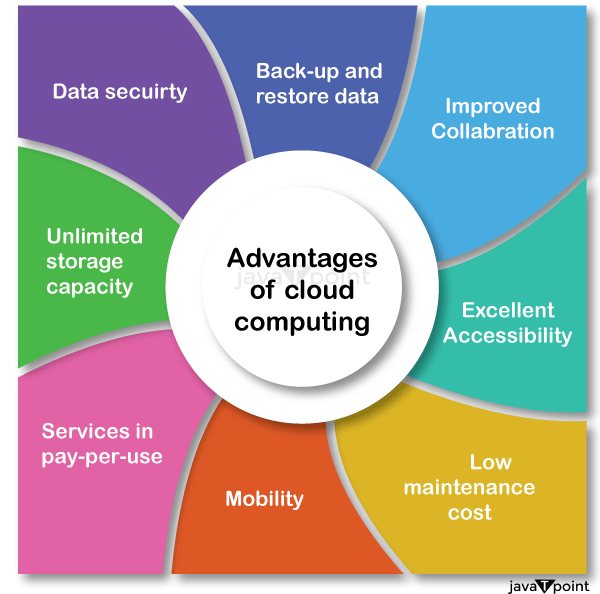
1) Back-up and restore data
Once the data is stored in the cloud, it is easier to get back-up and restore that data using the cloud.
2) Improved collaboration
Cloud applications improve collaboration by allowing groups of people to quickly and easily share information in the cloud via shared storage.
3) Excellent accessibility
Cloud allows us to quickly and easily access store information anywhere, anytime in the whole world, using an internet connection. An internet cloud infrastructure increases organization productivity and efficiency by ensuring that our data is always accessible.
4) Low maintenance cost
Cloud computing reduces both hardware and software maintenance costs for organizations.
5) Mobility
Cloud computing allows us to easily access all cloud data via mobile.
6) IServices in the pay-per-use model
Cloud computing offers Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to the users for access services on the cloud and pays the charges as per the usage of service.
7) Unlimited storage capacity
Cloud offers us a huge amount of storing capacity for storing our important data such as documents, images, audio, video, etc. in one place.
8) Data security
Data security is one of the biggest advantages of cloud computing. Cloud offers many advanced features related to security and ensures that data is securely stored and handled.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
A list of the disadvantage of cloud computing is given below -
1) Internet Connectivity
As you know, in cloud computing, every data (image, audio, video, etc.) is stored on the cloud, and we access these data through the cloud by using the internet connection. If you do not have good internet connectivity, you cannot access these data. However, we have no any other way to access data from the cloud.
2) Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in is the biggest disadvantage of cloud computing. Organizations may face problems when transferring their services from one vendor to another. As different vendors provide different platforms, that can cause difficulty moving from one cloud to another.
3) Limited Control
As we know, cloud infrastructure is completely owned, managed, and monitored by the service provider, so the cloud users have less control over the function and execution of services within a cloud infrastructure.
4) Security
Although cloud service providers implement the best security standards to store important information. But, before adopting cloud technology, you should be aware that you will be sending all your organization's sensitive information to a third party, i.e., a cloud computing service provider. While sending the data on the cloud, there may be a chance that your organization's information is hacked by Hackers.
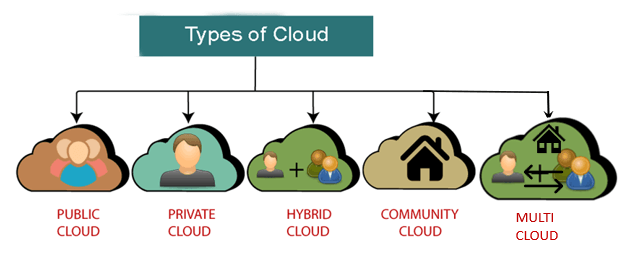
Types of Cloud
There are the following 4 types of cloud that you can deploy according to the organization's needs-
Public Cloud
Public cloud is open to all to store and access information via the Internet using the pay-per-usage method.
In public cloud, computing resources are managed and operated by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP).
Example: Amazon elastic compute cloud (EC2), IBM SmartCloud Enterprise, Microsoft, Google App Engine, Windows Azure Services Platform.
Advantages of Public Cloud
There are the following advantages of Public Cloud -
- Public cloud is owned at a lower cost than the private and hybrid cloud.
- Public cloud is maintained by the cloud service provider, so do not need to worry about the maintenance.
- Public cloud is easier to integrate. Hence it offers a better flexibility approach to consumers.
- Public cloud is location independent because its services are delivered through the internet.
- Public cloud is highly scalable as per the requirement of computing resources.
- It is accessible by the general public, so there is no limit to the number of users.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
- Public Cloud is less secure because resources are shared publicly.
- Performance depends upon the high-speed internet network link to the cloud provider.
- The Client has no control of data.
To Read More Click Here
Private Cloud
Private cloud is also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud. It is used by organizations to build and manage their own data centers internally or by the third party. It can be deployed using Opensource tools such as Openstack and Eucalyptus.
Based on the location and management, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) divide private cloud into the following two parts-
- On-premise private cloud
- Outsourced private cloud
Advantages of Private Cloud
There are the following advantages of the Private Cloud -
- Private cloud provides a high level of security and privacy to the users.
- Private cloud offers better performance with improved speed and space capacity.
- It allows the IT team to quickly allocate and deliver on-demand IT resources.
- The organization has full control over the cloud because it is managed by the organization itself. So, there is no need for the organization to depends on anybody.
- It is suitable for organizations that require a separate cloud for their personal use and data security is the first priority.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Skilled people are required to manage and operate cloud services.
- Private cloud is accessible within the organization, so the area of operations is limited.
- Private cloud is not suitable for organizations that have a high user base, and organizations that do not have the prebuilt infrastructure, sufficient manpower to maintain and manage the cloud.
To Read More Click Here
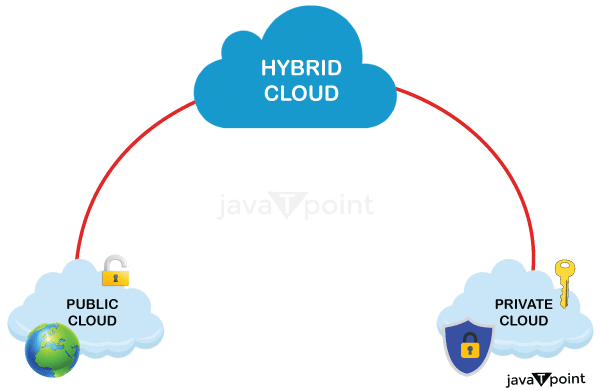
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud is a combination of the public cloud and the private cloud. we can say:
Hybrid Cloud = Public Cloud + Private Cloud
Hybrid cloud is partially secure because the services which are running on the public cloud can be accessed by anyone, while the services which are running on a private cloud can be accessed only by the organization's users.
Example: Google Application Suite (Gmail, Google Apps, and Google Drive), Office 365 (MS Office on the Web and One Drive), Amazon Web Services.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
There are the following advantages of Hybrid Cloud -
- Hybrid cloud is suitable for organizations that require more security than the public cloud.
- Hybrid cloud helps you to deliver new products and services more quickly.
- Hybrid cloud provides an excellent way to reduce the risk.
- Hybrid cloud offers flexible resources because of the public cloud and secure resources because of the private cloud.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
- In Hybrid Cloud, security feature is not as good as the private cloud.
- Managing a hybrid cloud is complex because it is difficult to manage more than one type of deployment model.
- In the hybrid cloud, the reliability of the services depends on cloud service providers.
To Read More Click Here
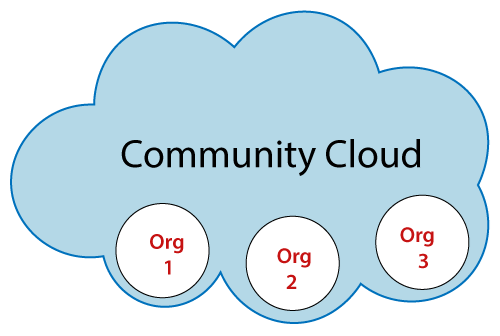
Community Cloud
Community cloud allows systems and services to be accessible by a group of several organizations to share the information between the organization and a specific community. It is owned, managed, and operated by one or more organizations in the community, a third party, or a combination of them.
Example: Health Care community cloud
Advantages of Community Cloud
There are the following advantages of Community Cloud -
- Community cloud is cost-effective because the whole cloud is being shared by several organizations or communities.
- Community cloud is suitable for organizations that want to have a collaborative cloud with more security features than the public cloud.
- It provides better security than the public cloud.
- It provdes collaborative and distributive environment.
- Community cloud allows us to share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other capabilities among various organizations.
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
- Community cloud is not a good choice for every organization.
- Security features are not as good as the private cloud.
- It is not suitable if there is no collaboration.
- The fixed amount of data storage and bandwidth is shared among all community members.
To Read More Click Here
Difference between public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud -
The below table shows the difference between public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
| Parameter | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Community Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host | Service provider | Enterprise (Third party) | Enterprise (Third party) | Community (Third party) |
| Users | General public | Selected users | Selected users | Community members |
| Access | Internet | Internet, VPN | Internet, VPN | Internet, VPN |
| Owner | Service provider | Enterprise | Enterprise | Community |
What Is A Cloud Deployment Model?
It works as your virtual computing environment with a choice of deployment model depending on how much data you want to store and who has access to the Infrastructure.
Different Types Of Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Most cloud hubs have tens of thousands of servers and storage devices to enable fast loading. It is often possible to choose a geographic area to put the data "closer" to users. Thus, deployment models for cloud computing are categorized based on their location. To know which model would best fit the requirements of your organization, let us first learn about the various types.
Public Cloud
The name says it all. It is accessible to the public. Public deployment models in the cloud are perfect for organizations with growing and fluctuating demands. It also makes a great choice for companies with low-security concerns. Thus, you pay a cloud service provider for networking services, compute virtualization & storage available on the public internet. It is also a great delivery model for the teams with development and testing. Its configuration and deployment are quick and easy, making it an ideal choice for test environments.
Benefits of Public Cloud
- Minimal Investment - As a pay-per-use service, there is no large upfront cost and is ideal for businesses who need quick access to resources
- No Hardware Setup - The cloud service providers fully fund the entire Infrastructure
- No Infrastructure Management - This does not require an in-house team to utilize the public cloud.
Limitations of Public Cloud
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns - Since it is accessible to all, it does not fully protect against cyber-attacks and could lead to vulnerabilities.
- Reliability Issues - Since the same server network is open to a wide range of users, it can lead to malfunction and outages
- Service/License Limitation - While there are many resources you can exchange with tenants, there is a usage cap.
Private Cloud
Now that you understand what the public cloud could offer you, of course, you are keen to know what a private cloud can do. Companies that look for cost efficiency and greater control over data & resources will find the private cloud a more suitable choice.
It means that it will be integrated with your data center and managed by your IT team. Alternatively, you can also choose to host it externally. The private cloud offers bigger opportunities that help meet specific organizations' requirements when it comes to customization. It's also a wise choice for mission-critical processes that may have frequently changing requirements.
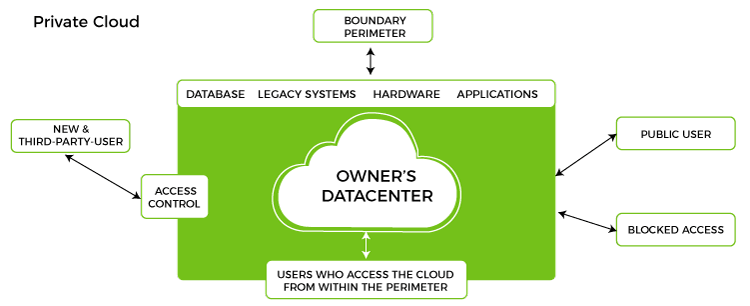
Benefits of Private Cloud
- Data Privacy - It is ideal for storing corporate data where only authorized personnel gets access
- Security - Segmentation of resources within the same Infrastructure can help with better access and higher levels of security.
- Supports Legacy Systems - This model supports legacy systems that cannot access the public cloud.
Limitations of Private Cloud
- Higher Cost - With the benefits you get, the investment will also be larger than the public cloud. Here, you will pay for software, hardware, and resources for staff and training.
- Fixed Scalability - The hardware you choose will accordingly help you scale in a certain direction
- High Maintenance - Since it is managed in-house, the maintenance costs also increase.
Community Cloud
The community cloud operates in a way that is similar to the public cloud. There's just one difference - it allows access to only a specific set of users who share common objectives and use cases. This type of deployment model of cloud computing is managed and hosted internally or by a third-party vendor. However, you can also choose a combination of all three.
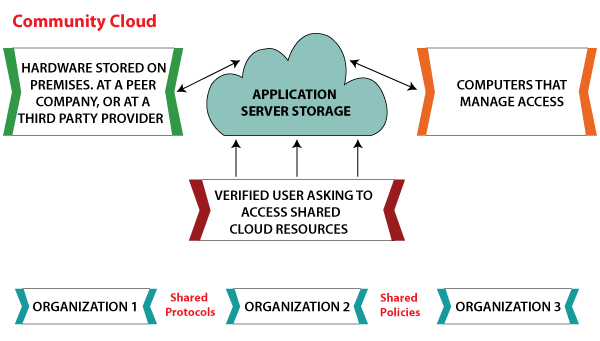
Benefits of Community Cloud
- Smaller Investment - A community cloud is much cheaper than the private & public cloud and provides great performance
- Setup Benefits - The protocols and configuration of a community cloud must align with industry standards, allowing customers to work much more efficiently.
Limitations of Community Cloud
- Shared Resources - Due to restricted bandwidth and storage capacity, community resources often pose challenges.
- Not as Popular - Since this is a recently introduced model, it is not that popular or available across industries
Hybrid Cloud
As the name suggests, a hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more cloud architectures. While each model in the hybrid cloud functions differently, it is all part of the same architecture. Further, as part of this deployment of the cloud computing model, the internal or external providers can offer resources.
Let's understand the hybrid model better. A company with critical data will prefer storing on a private cloud, while less sensitive data can be stored on a public cloud. The hybrid cloud is also frequently used for 'cloud bursting'. It means, supposes an organization runs an application on-premises, but due to heavy load, it can burst into the public cloud.
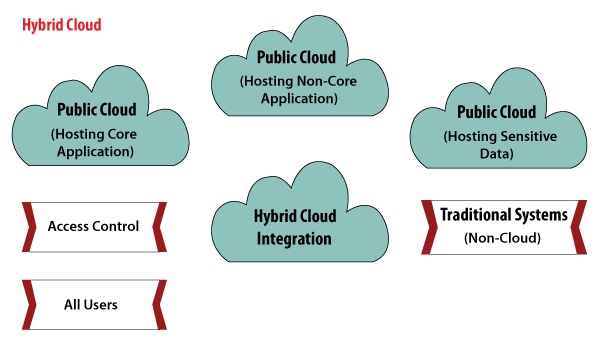
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Cost-Effectiveness - The overall cost of a hybrid solution decreases since it majorly uses the public cloud to store data.
- Security - Since data is properly segmented, the chances of data theft from attackers are significantly reduced.
- Flexibility - With higher levels of flexibility, businesses can create custom solutions that fit their exact requirements
Limitations of Hybrid Cloud
- Complexity - It is complex setting up a hybrid cloud since it needs to integrate two or more cloud architectures
- Specific Use Case - This model makes more sense for organizations that have multiple use cases or need to separate critical and sensitive data
A Comparative Analysis of Cloud Deployment Models
With the below table, we have attempted to analyze the key models with an overview of what each one can do for you:
| Important Factors to Consider | Public | Private | Community | Hybrid |
| Setup and ease of use | Easy | Requires professional IT Team | Requires professional IT Team | Requires professional IT Team |
| Data Security and Privacy | Low | High | Very High | High |
| Scalability and flexibility | High | High | Fixed requirements | High |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Most affordable | Most expensive | Cost is distributed among members | Cheaper than private but more expensive than public |
| Reliability | Low | High | Higher | High |
Making the Right Choice for Cloud Deployment Models
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to picking a cloud deployment model. Instead, organizations must select a model based on workload-by-workload. Start with assessing your needs and consider what type of support your application requires. Here are a few factors you can consider before making the call:
- Ease of Use - How savvy and trained are your resources? Do you have the time and the money to put them through training?
- Cost - How much are you willing to spend on a deployment model? How much can you pay upfront on subscription, maintenance, updates, and more?
- Scalability - What is your current activity status? Does your system run into high demand?
- Compliance - Are there any specific laws or regulations in your country that can impact the implementation? What are the industry standards that you must adhere to?
- Privacy - Have you set strict privacy rules for the data you gather?
Each cloud deployment model has a unique offering and can immensely add value to your business. For small to medium-sized businesses, a public cloud is an ideal model to start with. And as your requirements change, you can switch over to a different deployment model. An effective strategy can be designed depending on your needs using the cloud mentioned above deployment models.
3 Service Models of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing makes it possible to render several services, defined according to the roles, service providers, and user companies. Cloud computing models and services are broadly classified as below:
IAAS: Changing Its Hardware Infrastructure on Demand
The Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS) means the hiring & utilizing of the Physical Infrastructure of IT (network, storage, and servers) from a third-party provider. The IT resources are hosted on external servers, and users can access them via an internet connection.
The Benefits
- Time and cost savings: No installation and maintenance of IT hardware in-house,
- Better flexibility: On-demand hardware resources that can be tailored to your needs,
- Remote access and resource management.
For Who?
This cloud computing service model is ideal for large accounts, enterprises, or organizations to build and manage their own IT platforms. However, they want the flexibility to amend their Infrastructure according to their needs.
PAAS: Providing a Flexible Environment for Your Software Applications
Platform as a Service (PAAS) allows outsourcing of hardware infrastructure and software environment, including databases, integration layers, runtimes, and more.
The Benefits
- Focus on development: Mastering the installation and development of software applications.
- Time saving and flexibility: no need to manage the implementation of the platform, instant production.
- Data security: You control the distribution, protection, and backup of your business data.
For Who?
It is ideal for companies wanting to maintain control over their business applications. However, they wish to get rid of constraints to manage the hardware infrastructure and software environment.
SAAS: Releasing the User Experience of Management Constraints
Software as a Service (SaaS) is provided over the internet and requires no prior installation. The services can be availed from any part of the world at a minimal per-month fee.
The Benefits
- You are entirely free from the infrastructure management and aligning software environment: no installation or software maintenance.
- You benefit from automatic updates with the guarantee that all users have the same software version.
- It enables easy and quicker testing of new software solutions.
For Who?
SAAS model accounts for 60% of sales of cloud solutions. Hence, it is applicable and preferred by most companies.
Cloud Computing Architecture
As we know, cloud computing technology is used by both small and large organizations to store the information in cloud and access it from anywhere at anytime using the internet connection.
Cloud computing architecture is a combination of service-oriented architecture and event-driven architecture.
Cloud computing architecture is divided into the following two parts -
- Front End
- Back End
The below diagram shows the architecture of cloud computing -
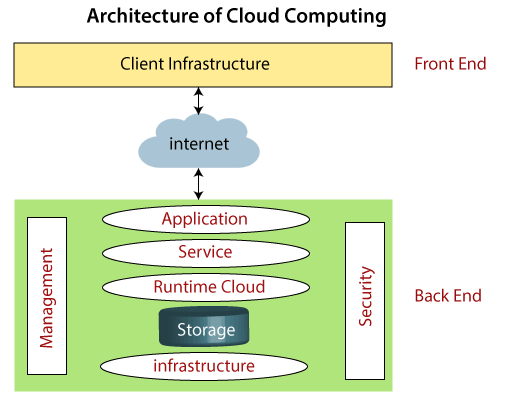
Front End
The front end is used by the client. It contains client-side interfaces and applications that are required to access the cloud computing platforms. The front end includes web servers (including Chrome, Firefox, internet explorer, etc.), thin & fat clients, tablets, and mobile devices.
Back End
The back end is used by the service provider. It manages all the resources that are required to provide cloud computing services. It includes a huge amount of data storage, security mechanism, virtual machines, deploying models, servers, traffic control mechanisms, etc.
Note: Both front end and back end are connected to others through a network, generally using the internet connection.
Components of Cloud Computing Architecture
There are the following components of cloud computing architecture -
1. Client Infrastructure
Client Infrastructure is a Front end component. It provides GUI (Graphical User Interface) to interact with the cloud.
2. Application
The application may be any software or platform that a client wants to access.
3. Service
A Cloud Services manages that which type of service you access according to the client’s requirement.
Cloud computing offers the following three type of services:
i. Software as a Service (SaaS) – It is also known as cloud application services. Mostly, SaaS applications run directly through the web browser means we do not require to download and install these applications. Some important example of SaaS is given below –
Example: Google Apps, Salesforce Dropbox, Slack, Hubspot, Cisco WebEx.
ii. Platform as a Service (PaaS) – It is also known as cloud platform services. It is quite similar to SaaS, but the difference is that PaaS provides a platform for software creation, but using SaaS, we can access software over the internet without the need of any platform.
Example: Windows Azure, Force.com, Magento Commerce Cloud, OpenShift.
iii. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – It is also known as cloud infrastructure services. It is responsible for managing applications data, middleware, and runtime environments.
Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Cisco Metapod.
4. Runtime Cloud
Runtime Cloud provides the execution and runtime environment to the virtual machines.
5. Storage
Storage is one of the most important components of cloud computing. It provides a huge amount of storage capacity in the cloud to store and manage data.
6. Infrastructure
It provides services on the host level, application level, and network level. Cloud infrastructure includes hardware and software components such as servers, storage, network devices, virtualization software, and other storage resources that are needed to support the cloud computing model.
7. Management
Management is used to manage components such as application, service, runtime cloud, storage, infrastructure, and other security issues in the backend and establish coordination between them.
8. Security
Security is an in-built back end component of cloud computing. It implements a security mechanism in the back end.
9. Internet
The Internet is medium through which front end and back end can interact and communicate with each other.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
As we all know that Cloud computing is trending technology. Almost every company switched their services on the cloud to rise the company growth.
Here, we are going to discuss some important advantages of Cloud Computing-

1) Back-up and restore data
Once the data is stored in the cloud, it is easier to get back-up and restore that data using the cloud.
2) Improved collaboration
Cloud applications improve collaboration by allowing groups of people to quickly and easily share information in the cloud via shared storage.
3) Excellent accessibility
Cloud allows us to quickly and easily access store information anywhere, anytime in the whole world, using an internet connection. An internet cloud infrastructure increases organization productivity and efficiency by ensuring that our data is always accessible.
4) Low maintenance cost
Cloud computing reduces both hardware and software maintenance costs for organizations.
5) Mobility
Cloud computing allows us to easily access all cloud data via mobile.
6) IServices in the pay-per-use model
Cloud computing offers Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to the users for access services on the cloud and pays the charges as per the usage of service.
7) Unlimited storage capacity
Cloud offers us a huge amount of storing capacity for storing our important data such as documents, images, audio, video, etc. in one place.
8) Data security
Data security is one of the biggest advantages of cloud computing. Cloud offers many advanced features related to security and ensures that data is securely stored and handled.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
A list of the disadvantage of cloud computing is given below -
1) Internet Connectivity
As you know, in cloud computing, every data (image, audio, video, etc.) is stored on the cloud, and we access these data through the cloud by using the internet connection. If you do not have good internet connectivity, you cannot access these data. However, we have no any other way to access data from the cloud.
2) Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in is the biggest disadvantage of cloud computing. Organizations may face problems when transferring their services from one vendor to another. As different vendors provide different platforms, that can cause difficulty moving from one cloud to another.
3) Limited Control
As we know, cloud infrastructure is completely owned, managed, and monitored by the service provider, so the cloud users have less control over the function and execution of services within a cloud infrastructure.
4) Security
Although cloud service providers implement the best security standards to store important information. But, before adopting cloud technology, you should be aware that you will be sending all your organization's sensitive information to a third party, i.e., a cloud computing service provider. While sending the data on the cloud, there may be a chance that your organization's information is hacked by Hackers.
Load Balancing in Cloud Computing
Load balancing is the method that allows you to have a proper balance of the amount of work being done on different pieces of device or hardware equipment. Typically, what happens is that the load of the devices is balanced between different servers or between the CPU and hard drives in a single cloud server.
Load balancing was introduced for various reasons. One of them is to improve the speed and performance of each single device, and the other is to protect individual devices from hitting their limits by reducing their performance.
Cloud load balancing is defined as dividing workload and computing properties in cloud computing. It enables enterprises to manage workload demands or application demands by distributing resources among multiple computers, networks or servers. Cloud load balancing involves managing the movement of workload traffic and demands over the Internet.
Traffic on the Internet is growing rapidly, accounting for almost 100% of the current traffic annually. Therefore, the workload on the servers is increasing so rapidly, leading to overloading of the servers, mainly for the popular web servers. There are two primary solutions to overcome the problem of overloading on the server-
- First is a single-server solution in which the server is upgraded to a higher-performance server. However, the new server may also be overloaded soon, demanding another upgrade. Moreover, the upgrading process is arduous and expensive.
- The second is a multiple-server solution in which a scalable service system on a cluster of servers is built. That's why it is more cost-effective and more scalable to build a server cluster system for network services.
Cloud-based servers can achieve more precise scalability and availability by using farm server load balancing. Load balancing is beneficial with almost any type of service, such as HTTP, SMTP, DNS, FTP, and POP/IMAP.
It also increases reliability through redundancy. A dedicated hardware device or program provides the balancing service.
Types of Load Balancing
You will need to understand the different types of load balancing for your network. Server load balancing is for relational databases, global server load balancing is for troubleshooting in different geographic locations, and DNS load balancing ensures domain name functionality. Load balancing can also be based on cloud-based balancers.
Network Load Balancing
Cloud load balancing takes advantage of network layer information and leaves it to decide where network traffic should be sent. This is accomplished through Layer 4 load balancing, which handles TCP/UDP traffic. It is the fastest local balancing solution, but it cannot balance the traffic distribution across servers.
HTTP(S) load balancing
HTTP(s) load balancing is the oldest type of load balancing, and it relies on Layer 7. This means that load balancing operates in the layer of operations. It is the most flexible type of load balancing because it lets you make delivery decisions based on information retrieved from HTTP addresses.
Internal Load Balancing
It is very similar to network load balancing, but is leveraged to balance the infrastructure internally.
Load balancers can be further divided into hardware, software and virtual load balancers.
Hardware Load Balancer
It depends on the base and the physical hardware that distributes the network and application traffic. The device can handle a large traffic volume, but these come with a hefty price tag and have limited flexibility.
Software Load Balancer
It can be an open source or commercial form and must be installed before it can be used. These are more economical than hardware solutions.
Virtual Load Balancer
It differs from a software load balancer in that it deploys the software to the hardware load-balancing device on the virtual machine.
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
A Service-Oriented Architecture or SOA is a design pattern which is designed to build distributed systems that deliver services to other applications through the protocol. It is only a concept and not limited to any programming language or platform.
What is Service?
A service is a well-defined, self-contained function that represents a unit of functionality. A service can exchange information from another service. It is not dependent on the state of another service. It uses a loosely coupled, message-based communication model to communicate with applications and other services.
Service Connections
The figure given below illustrates the service-oriented architecture. Service consumer sends a service request to the service provider, and the service provider sends the service response to the service consumer. The service connection is understandable to both the service consumer and service provider.

Service-Oriented Terminologies
Let's see some important service-oriented terminologies:
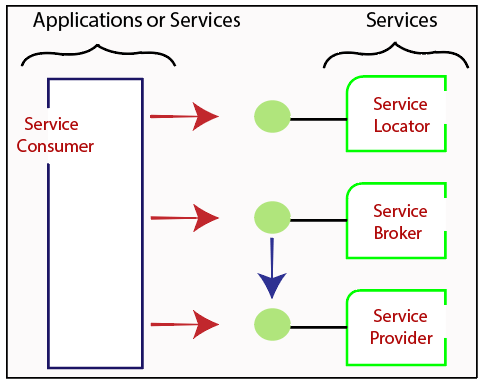
- Services - The services are the logical entities defined by one or more published interfaces.
- Service provider - It is a software entity that implements a service specification.
- Service consumer - It can be called as a requestor or client that calls a service provider. A service consumer can be another service or an end-user application.
- Service locator - It is a service provider that acts as a registry. It is responsible for examining service provider interfaces and service locations.
- Service broker - It is a service provider that pass service requests to one or more additional service providers.
Characteristics of SOA
The services have the following characteristics:
- They are loosely coupled.
- They support interoperability.
- They are location-transparent
- They are self-contained.
Components of service-oriented architecture
The service-oriented architecture stack can be categorized into two parts - functional aspects and quality of service aspects.
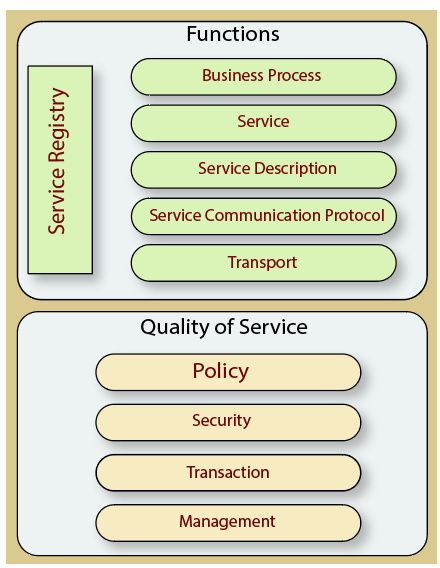
Functional aspects
The functional aspect contains:
- Transport - It transports the service requests from the service consumer to the service provider and service responses from the service provider to the service consumer.
- Service Communication Protocol - It allows the service provider and the service consumer to communicate with each other.
- Service Description - It describes the service and data required to invoke it.
- Service - It is an actual service.
- Business Process - It represents the group of services called in a particular sequence associated with the particular rules to meet the business requirements.
- Service Registry - It contains the description of data which is used by service providers to publish their services.
Quality of Service aspects
The quality of service aspects contains:
- Policy - It represents the set of protocols according to which a service provider make and provide the services to consumers.
- Security - It represents the set of protocols required for identification and authorization.
- Transaction - It provides the surety of consistent result. This means, if we use the group of services to complete a business function, either all must complete or none of the complete.
- Management - It defines the set of attributes used to manage the services.
Advantages of SOA
SOA has the following advantages:
- Easy to integrate - In a service-oriented architecture, the integration is a service specification that provides implementation transparency.
- Manage Complexity - Due to service specification, the complexities get isolated, and integration becomes more manageable.
- Platform Independence - The services are platform-independent as they can communicate with other applications through a common language.
- Loose coupling - It facilitates to implement services without impacting other applications or services.
- Parallel Development - As SOA follows layer-based architecture, it provides parallel development.
- Available - The SOA services are easily available to any requester.
- Reliable - As services are small in size, it is easier to test and debug them.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization is the "creation of a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as a server, a desktop, a storage device, an operating system or network resources".
In other words, Virtualization is a technique, which allows to share a single physical instance of a resource or an application among multiple customers and organizations. It does by assigning a logical name to a physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource when demanded.
What is the concept behind the Virtualization?
Creation of a virtual machine over existing operating system and hardware is known as Hardware Virtualization. A Virtual machine provides an environment that is logically separated from the underlying hardware.
The machine on which the virtual machine is going to create is known as Host Machine and that virtual machine is referred as a Guest Machine
Types of Virtualization:
- Hardware Virtualization.
- Operating system Virtualization.
- Server Virtualization.
- Storage Virtualization.
1) Hardware Virtualization:
When the virtual machine software or virtual machine manager (VMM) is directly installed on the hardware system is known as hardware virtualization.
The main job of hypervisor is to control and monitoring the processor, memory and other hardware resources.
After virtualization of hardware system we can install different operating system on it and run different applications on those OS.
Usage:
Hardware virtualization is mainly done for the server platforms, because controlling virtual machines is much easier than controlling a physical server.
2) Operating System Virtualization:
When the virtual machine software or virtual machine manager (VMM) is installed on the Host operating system instead of directly on the hardware system is known as operating system virtualization.
Usage:
Operating System Virtualization is mainly used for testing the applications on different platforms of OS.
3) Server Virtualization:
When the virtual machine software or virtual machine manager (VMM) is directly installed on the Server system is known as server virtualization.
Usage:
Server virtualization is done because a single physical server can be divided into multiple servers on the demand basis and for balancing the load.
4) Storage Virtualization:
Storage virtualization is the process of grouping the physical storage from multiple network storage devices so that it looks like a single storage device.
Storage virtualization is also implemented by using software applications.
Usage:
Storage virtualization is mainly done for back-up and recovery purposes.
How does virtualization work in cloud computing?
Virtualization plays a very important role in the cloud computing technology, normally in the cloud computing, users share the data present in the clouds like application etc, but actually with the help of virtualization users shares the Infrastructure.
The main usage of Virtualization Technology is to provide the applications with the standard versions to their cloud users, suppose if the next version of that application is released, then cloud provider has to provide the latest version to their cloud users and practically it is possible because it is more expensive.
To overcome this problem we use basically virtualization technology, By using virtualization, all severs and the software application which are required by other cloud providers are maintained by the third party people, and the cloud providers has to pay the money on monthly or annual basis.
Conclusion
Mainly Virtualization means, running multiple operating systems on a single machine but sharing all the hardware resources. And it helps us to provide the pool of IT resources so that we can share these IT resources in order get benefits in the business.
What is Cloud Cube Model?
Cloud Cube model, helps to categorize the cloud network based on the four-dimensional factor. Their main focus is to protect and secure the cloud network. This cloud cube model helps to select cloud formation for secure collaboration.
This model helps IT managers, organizations, and business leaders by providing the secure and protected network.
Security is an important concern for cloud customers and most of the cloud providers understand it. The customer should also keep in mind, the selected cloud formation meets the regulatory and location requirements.
They should also keep in mind that if cloud providers stop providing the services, where else they can move. There are three service models, which include:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
In addition, there are four deployment models such as:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
These models are very flexible Agile and responsible. They are user-friendly and provide many benefits to the customers.
How to Secure Data in the Cloud Cube Model?
There are some steps and points to keep in mind before securing your data in a cloud cube model:
- Step 1
The classification of the data, the customer should know what rules must be applied to protect it.
- Step 2
It should be ensured, the data exist only in specific trust levels.
- Step 3
It should check that what regulatory compliance and restrictions are applicable. For example, the data should stay in a particular boundary and whether it has to stay in the safe harbour or not.
After the data is classified and is ready to put in the required zone, the assigned person is in a position to decide the following factors-
- The data and processes, which are to be moved in the cloud.
- At what level the user wants to operate in the cloud. It can be infrastructure, platform, software, or platform as a service.
- The cloud formations, which are mostly compatible as per the requirement.
- The level of operation in the cloud can be different as per the requirement.
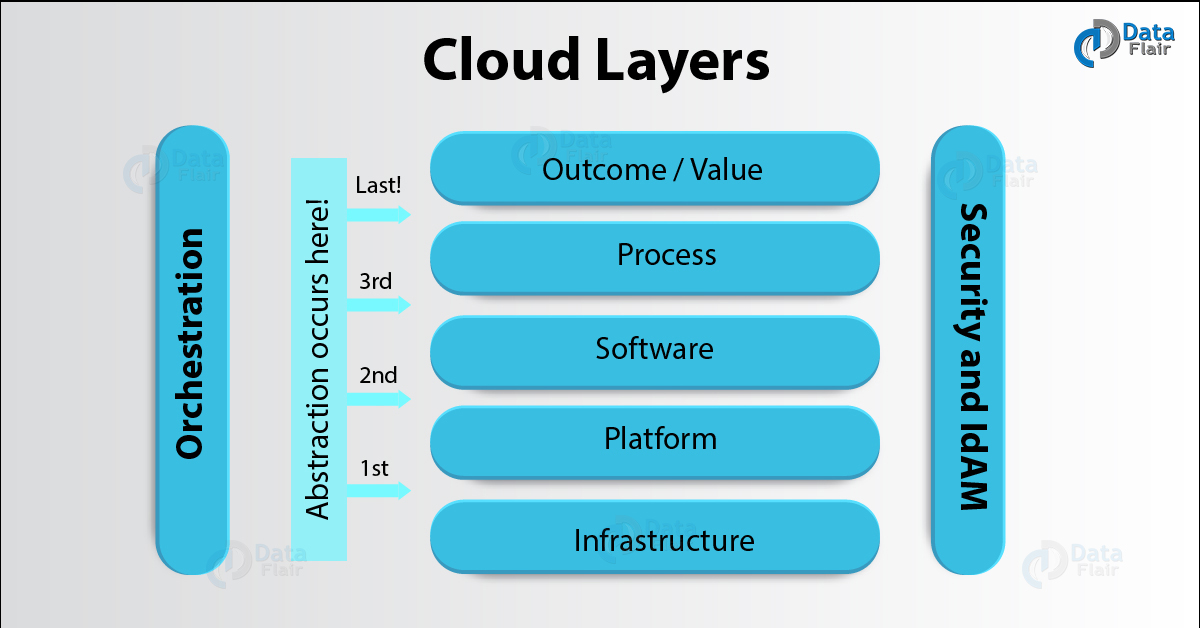
Below is the chart which shows the Cloud layers, where the cloud operates.
After that, there are forms of cloud and the user can store the data which is mostly compatible with the company.
Dimensions of Cloud Cube Model
Cloud Cube model has four dimensions to categorized cloud formations:
- Internal/External
- Proprietary/Open
- De-Perimeterized/Perimeterized
- Insourced/Outsourced Dimension
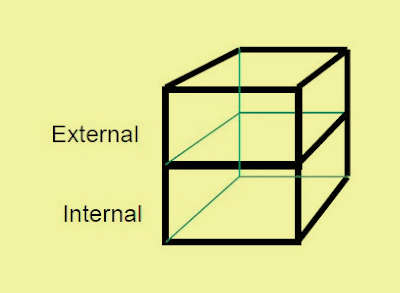
i. Internal/External
The most basic cloud form is the external and internal cloud form. The external or internal dimension defines the physical location of the data. It acknowledges us whether the data exists inside or outside of your organization’s boundary.
Here, the data which is stored using a private cloud deployment will be considered internal and data outside the cloud will be considered external.
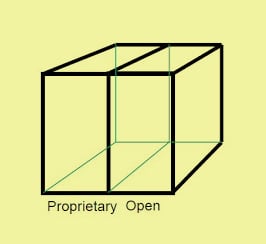
ii. Proprietary/Open
The second type of cloud formation is proprietary and open. The proprietary or open dimension states about the state of ownership of the cloud technology and interfaces. It also tells the degree of interoperability, while enabling data transportability between the system and other cloud forms.
The proprietary dimension means, that the organization providing the service is securing and protecting the data under their ownership.
The open dimension is using a technology in which there are more suppliers. Moreover, the user is not constrained in being able to share the data and collaborate with selected partners using the open technology.
iii. De-Perimeterized/Perimeterized
The third type of cloud formation is De-perimeterized and Perimeterized. To reach this form, the user needs collaboration oriented architecture and Jericho forum commandments.
The Perimeterised and De-perimeterized dimension tells us whether you are operating inside your traditional it mindset or outside it.
Perimeterized dimension means, continuing to operate within the traditional it boundary, orphan signaled by network firewalls.
With the help of VPN and operation of the virtual server in your own IP domain, the user can extend the organizations perimeter into external Cloud Computing domain. This means that the user is making use of the own services to control access.
De-perimeterized dimension means the system perimeter is architected on the principles outlined in the Jericho forums commandments. In De-perimeterized dimension, the data will be encapsulated with metadata and mechanisms, which will further help to protect the data and limit the inappropriate usage.
iv. Insourced/Outsourced
The Insourced and outsourced dimensions have two states in each of the eight cloud forms. In the outsourced dimension the services provided by the third party, whereas in the insourced dimension the services provided by the own staff under the control.
In this few organizations that are traditional bandwidth software or hardware, providers will run fluently on becoming cloud service providers.
The organizations which are seeking to procedure cloud services must have the ability to set legally binding collaboration agreement. In this, an organization should ensure that data is deleted from the service provider’s Infrastructure.
Cloud Hypervisor
The key is to enable hypervisor virtualization. In its simplest form, a hypervisor is specialized firmware or software, or both, installed on a single hardware that will allow you to host multiple virtual machines. This allows physical hardware to be shared across multiple virtual machines. The computer on which the hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called the host machine.
Virtual machines are called guest machines. The hypervisor allows the physical host machine to run various guest machines. It helps to get maximum benefit from computing resources such as memory, network bandwidth and CPU cycles.
Advantages of Hypervisor
Although virtual machines operate on the same physical hardware, they are isolated from each other. It also denotes that if one virtual machine undergoes a crash, error, or malware attack, it does not affect other virtual machines.
Another advantage is that virtual machines are very mobile because they do not depend on the underlying hardware. Since they are not connected to physical hardware, switching between local or remote virtualized servers becomes much easier than with traditional applications.
Types of Hypervisors in Cloud Computing
There are two main types of hypervisors in cloud computing.
Type I Hypervisor
A Type I hypervisor operates directly on the host's hardware to monitor the hardware and guest virtual machines, and is referred to as bare metal. Typically, they do not require the installation of software ahead of time.
Instead, you can install it directly on the hardware. This type of hypervisor is powerful and requires a lot of expertise to function well. In addition, Type I hypervisors are more complex and have few hardware requirements to run adequately. Because of this it is mostly chosen by IT operations and data center computing.
Examples of Type I hypervisors include Oracle VM Server for Xen, SPARC, Oracle VM Server for x86, Microsoft Hyper-V, and VMware's ESX/ESXi.
Type II Hypervisor
It is also called a hosted hypervisor because it is installed on an existing operating system, and they are not more capable of running more complex virtual tasks. People use it for basic development, testing and simulation.
If a security flaw is found inside the host OS, it can potentially compromise all running virtual machines. This is why Type II hypervisors cannot be used for data center computing, and they are designed for end-user systems where security is less of a concern. For example, developers can use a Type II hypervisor to launch virtual machines to test software products prior to their release.
NIST
Let’s take a step back and look at the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) definition of cloud computing. NIST is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce and works to promote the economy and public welfare by providing technical leadership for measurement and standards infrastructure. Industry expert and blogger Bernard Golden writes for CIO, “I think the National Institute of Standards and Technology has done a great service in codifying its definition [of cloud computing], and I rely on it to communicate the key characteristics of cloud computing — and, more importantly, to draw the distinctions between cloud computing and the traditional IT approach to infrastructure management.”
From the NIST definition of cloud computing, “Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interactive.” NIST provides the following definitions of the essential characteristics and service and deployment models for cloud computing.
Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics:
- On-demand self-service: consumers can unilaterally provision computing capabilities as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad network access: capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanism that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms.
- Resources pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand
- Rapid elasticity: capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand.
- Measured service: cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service.
Service Models
- Software as a Service (Saas)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Deployment Models
- Private cloud
- Community cloud
- Public cloud
- Hybrid cloud
As the array of cloud computing solutions and services continues to grow, the NIST definition of cloud computing grounds our understanding of what cloud can offer versus traditional IT solutions.


0 Comments